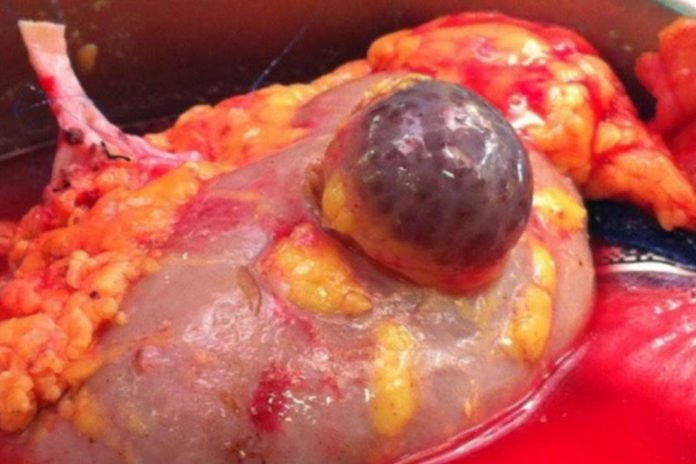
A cortical cyst is a fluid sac that begins forming in your kidneys. Traditionally, the renal cysts are characterized as plain cysts, which usually mean that they come with a very thin wall, and often contain a water-like fluid in them. The cysts are very common among the older people, and are not know to cause any harm on appearance.
Given that a cortical cyst rarely shows any symptoms, doctors often identify them when performing imaging tests. There are renal cysts that may appear to be more complex, given that they have thicker walls, or because they contain solid materials in them instead of the fluids.
As such, the physician may need to perform more imaging tests in a bid to monitor the complex cysts, and be in a position to differentiate the benign cysts from cancer. Some of the tests that are performed by the doctor in order to achieve this include abdominal and pelvic CT, pelvic or abdominal ultrasound, or a full body MRI.
A cortical cyst will in many cases be left alone, and will not require any kind of medical attention, unless it is harming the functioning of your kidney, or is causing the appearance of symptoms. In cases where treatment is needed, the doctor may use surgery or sclerotherapy to completely drain this cyst, as well as take preventive measures to ensure that it will not recur in the future.
What is a cortical cyst?
A cortical cyst is a common type of kidney cyst, which is also known as renal cortical cyst. It is normally found at the renal cortex, hence its name. Its prognosis is relatively better, which makes it easier to treat, especially given that it is located on the outer part of your kidneys.
Even though they normally do not require treatment, there are rare cases where they may need to be treated, due to issues to do with enlargement, infection, or bleeding. When this kind of complications takes place, the accompanying symptoms may include:
- Upper abdominal pain
- Fever
- Pain or tenderness between the pelvis and the ribs
- A change in your urinary habits
- Presence of blood in your urine
The primacy cause of the cysts is not known, although doctors believe age to be a big risk factor. According to Mayo Clinic, one-third of all old people above the age of seventy years have at least one or more simple renal cysts in their kidney. With increasing age, it is deemed normal to have more than one cyst in each of your kidneys.
You should note that having a few renal cysts is very different from having many cysts in your kidneys because of a condition known as polycystic renal disease (PKD). This is a genetic disorder that is characterized by the appearance of cysts in your kidneys, which in turn impair the functioning of your kidneys.
What causes renal cortical kidney cysts?
To-date, the exact cause of this condition has remained unclear. Doctors believe that apart from age, it can also be caused by congenital abnormal structure of renal tubules and glomeruli, or it can also be caused by injuries or infections. However, the primary causes have something to do with gender and age. Studies have shown that there are more male patients treated with this condition as opposed to their female counterparts.
What are its symptoms?
Normally, when the cortical cyst is less than 3cm, a patient will not display any obvious symptoms, and will not experience any kind of discomfort. Often, the doctors find the renal cysts purely by accident when performing imaging tests such as MRI, ultrasound, and CT or when performing a physical examination.
If a cyst continues to grow and enlarge, a patient can exhibit the following symptoms:
- Discomfort and pain in the lower back as well as the abdomen: normally, the pain is dull in nature, and is fixed on one or both sides of the abdomen, and will normally radiate in a downward manner
- Presence of an abdominal mass-once the cysts becomes large enough, a patient may start to feel the presence of a palpable mass on either side of the abdomen
- Proteinuria—this is where a patient starts to see bubbles in their urine, and normally, small amounts of protein can be detected in the urine
- Hematuria—this is where a patient notices blood in the urine, or the blood may be noticed when the urine is placed under a microscope for observation purposes
- Hypertension—when the renal cortical cyst is oppressed, it can cause isichemia as well as the increased secretion of renin.
What are the kidney functions?
Normally, the human body comes with two kidneys, with one being available on each side of the middle back, just below the ribs. Your kidney is normally the size of your fist. Its functions include:
- Controlling the amount of salts and fluids present in your blood
- Filtering out all the body’s waste products
- Production of hormones that assist in controlling blood pressure, calcium levels, as well as the production of red-blood cells.
- Controlling your body chemistry to assist in maintaining salt, acid, and mineral balances in your blood stream.
Types of kidney cysts

Cystic kidney disease comes in three main forms:
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD)
Normally, this is an inherited condition. The presence of defective genes causes the cyst to start growing in your kidneys. In this case, both kidneys will be affected, but you may find one developing cysts much earlier than the other.
According to Healthline.com, PKD is one of the most common causes of kidney failures in Australia, and will normally affect men and women of different ethnic backgrounds. Currently, no cure has been found for this condition; however, the research into ways that can be used to prevent the growth of cysts, as well as slow down the decline of kidney functions is ongoing.
Medullary cystic kidney disease (MCKD)
The condition is also inherited. Here, the cysts will begin to form on the inner part of your kidney. When these happens, your kidneys will begin to shrink as the outer section starts to become thin. MCKD has been known to cause to kidney failure among people who are between the ages of twenty and fifty years.
In some of the reported cases, there has been no family history, which implies that genetic mutation may have taken place. One condition that is similar to MCKD is juvenile nephronophthisis, which is a childhood disease.
Medullary sponge kidney
In this case, the cyst will start developing in your urine-collecting tubules and ducts or either one kidney, or both of them. This condition could be present at birth (congenital), and there have been cases where it has been reported to run in the family of the affected person.
However, scientists have not been able to pinpoint whether this is caused by genetic mutation, or it is because the condition is inherited. Currently, its exact cause is yet to be identified, and there is no known cure for it. Kidney failure among people suffering from this condition is rare, though it may develop because of kidney stones or repeated infections, which are known to occur together with the condition.
Diagnosis of cortical cyst
Given that a cortical cyst rarely causes any symptoms, it is mostly identified when a doctor is performing an imaging test for one reason or another. If the doctor suspects that you have a cystic kidney disease, he or she may recommend a series of tests, depending on the condition that has been suspected. Normally, the diagnostic tests that are performed could include:
- Physical examination used to detect enlarged kidneys and high blood pressure
- Urine tests – meant to look for protein or blood in your urine
- Blood tests – aimed at assessing your kidney functioning
- Genetic testing – it is normally used for family related tests, and is therefore not a routine test
- Renal ultrasound – this is a simple test, which relies on sound waves to assist the doctor detect the presence of cysts in your kidneys. It is very good at identifying even the smallest of cysts
- Computer tomography(CT) and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging scans – these scans can be used to detect even the smallest of cysts. The scans may become necessary when the ultrasound results are deemed to be inconclusive, or if your doctor requires more information.
Cortical cyst home remedies
Cortical cyst is a condition where fluid-filled cysts begin developing in your renal cortex. You should note that this is the functional part of your whole kidney. For a person with this kind of condition, the home remedies will play a vital role in helping you maintain your overall health. The home remedies include:
Food therapy
Regardless of the condition afflicting a patient, food therapy comes in handy in ensuring that the patient remains healthy at all times, and that they start regaining their health sooner rather than later. A person with renal cysts is always advised to ensure that they do not consume high-salt foods, beer and alcohol, extra meat, as well as low quality proteins. It is important to make sure that each patient has a personalized diet plan, which is based on his or her medical condition.
Exercises
Performing moderate exercises each day assists in strengthening a patient’s body, while at the same time boosting their immunity. An improved immunity comes in handy as it helps the body fight off infections, as well as keep the blood pressure under control.
It is however important to ensure that a patient with renal cyst does not perform exercises that are deemed to be strenuous. This may include bending and stretching movement. Avoid strenuous exercises helps prevent the kidney cyst from rupturing. Therefore, if you are to exercise, make sure you only perform light or gentle exercises.
Foot bath
Many individuals, especially those with advanced ages are advised to take foot baths on a regular basis. A foot bath comes with many health benefits, such as assisting in improving your blood circulation, boosting the body’s defense mechanism, as well as slowing down the progress of the renal cysts. You can ask for advice from your doctor on how to go about adding some herbal medicine to the footbath.
Hot compress
It is a type of therapy that can be practiced at home and in the hospital as well. By placing herbal medicines on the patients Shenshu acupoint. It is a corresponding acupoint of your kidney, which makes it possible to shrink your kidney cysts, and this will assist in protecting the functioning of your kidneys.
Cortical cyst in kidney treatment
There is no known cure for cortical cyst. The medical treatment that is available is mainly aimed at managing the symptoms manifested by the condition, as well as reducing the risk of a patient developing complications. The treatment prescribed by the doctor will often depend on factors such as:
- Severity of your condition
- Kind of cortical cyst disease that you have
- Whether you are having complications or not
- Type and severity of your complications
- Whether the kidneys are failing or not
- Current age, and status of your overall health
Having looked at the above factors, the doctor may prescribe treatment, which may include dietary and lifestyle changes. Currently, there are developments that have been made on the research being conducted on how to prevent cystic growth in patients with PKD.
Several states in Australia have begun running trials on medications that are believed to have the capabilities to stop your sacs from getting filled with fluids. A recent study published in 2015 showed promising results for medication that stops that growth and development of the cysts, while at the same time slowing down the decline of your kidney functions.
References;
- http://www.pkdclinic.org/kidney-cyst-overview/529.html
- http://www.med-health.net/Cortical-Cyst.html
- http://www.kidney-cares.org/kidney-cyst-symptoms-complications/985.html
- http://www.kidney-symptom.com/kidney-cyst-treatment/176.html