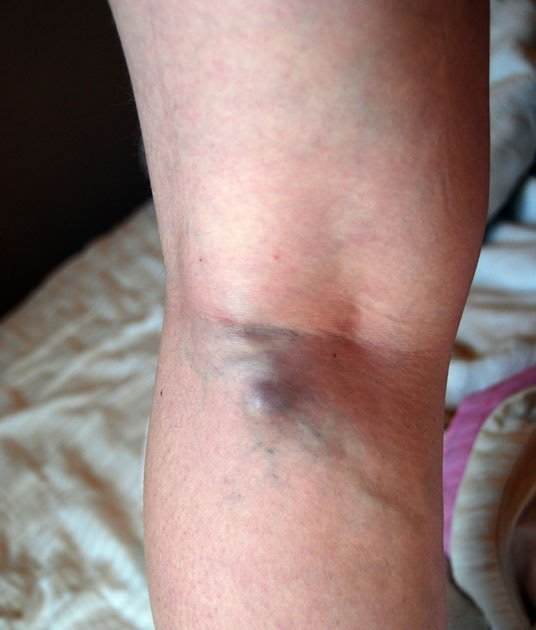
A blood clot behind the knee can cause sharp pain at the back of the leg. In most cases, clots are complications of orthopedic surgeries like joint replacement or those carried out to repair the knee, hip, or other joints, says Claudette Lajam MD, Everyday Health. A blood clot can stop the average circulation of blood in your body. Here are some of the symptoms you need to be on the lookout for, the cause you will need to avoid, and treatment options available in case of a blood clot. According to Dr. Claudette, more than half a million people in the United States alone are affected by venous thromboembolism each year. This involves diseases such as deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. With deep vein thrombosis, a blood clot develops in the deep vein. This is common in the leg. This kind of blood clot can result in illness, disability, and even death if not diagnosed and treated in time. Pulmonary embolism, on the other hand, is a serious complication of deep vein thrombosis. This complication occurs when part of the clot breaks up and travels through your bloodstream to your lung.
What does a blood clot behind the knee feel like?
A blood clot can occur on any of your blood vessels. When a blood clot occurs in one of your veins, it is called venous thromboembolism. A blood clot on any part of your body is a serious issue, and it should be treated as such. It can be life-threatening, and as such immediate medical attention is required. Research by the center for disease control and prevention CDC, an estimated 100,000 people die from this condition. So what does a blood clot behind the knee feel like? The symptoms of a blood clot will vary from one person to the other, depending on how severe the condition is. In some cases, it is possible to have a blood clot with no symptoms. In any case or instance, if you are slightly concerned that you might have a blood clot, you need to see your healthcare provider as soon as possible. A blood clot occurring behind the knee and other major veins in your body is known as deep vein thrombosis. This kind of blood clot may occur in one of your legs or around the hip region. While the existence of the clot alone may not harm you, the clot could break loose and end up in your lungs. This is what leads to a serious and possibly fatal condition known as pulmonary embolism PE. A blood clot behind the knee may feel numb and painful. Blood clots in vein commonly just under the skin, as said, are often not harmless, most will clear up on their own within a month. Proper treatment can ease the pain and discomfort caused by a blood clot in the back of the knee.
Pictures
What does a blood clot at the back of the leg look like? Here are pictures and photos to help you identify your problem.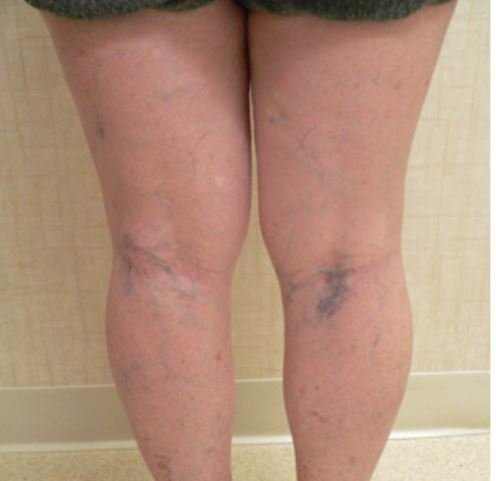
Causes of blood clots behind the knee
A blood clot behind the knee or what is often referred to as deep vein thrombosis is a clot that develops within the deep vein in the body. This clot is common in the leg. Behind the knee, a blood clot occurs inside the deep leg vein, a large vein that runs through the muscles of the calf and your thigh. As mentioned, a blood clot can cause pain and swelling in the leg if left unattended. The clot may also lead to complications such as pulmonary embolism, a serious condition that often occurs when a part of the blood clot breaks and blocks one of the blood vessels in the lungs. The risk of getting a blood clot increases as you age. The condition can also be inherited from a parent. This makes the condition common and more prone to some people. Some of the possible causes of a blood clot behind the knee would include the following:
- Major surgery
- Long-distance traveling
- Obesity
- Varicose veins
- Heart or lung problems
- Major injuries
- Cancer
- Pregnancy and childbirth
- Hormone fluctuation (estrogen-containing contraceptive pills patch vaginal ring)
- Leg paralysis
- Replacement therapy
- Immobility such prolonged bed rest
- A slow flow of blood
Can blood clots in knee cap be deep vein thrombosis (DVT)?
Is there any difference between deep vein thrombosis and a blood clot behind the knee? According to Stuart T. Haines, Phar.D., a deep vein thrombosis can be a potentially deadly condition caused by a blood clot that forms in a vein. DVT is common in the deep vein in the legs. DVT is a common condition affecting close to two million people in the United States alone, every year. A deep vein thrombosis or a blood clot behind the knee happens as a result of the slow flow of blood in the veins when the blood flow stops or due to damage to the veins. In many cases, a deep vein thrombosis will cause no symptoms. However, pain and swelling are the common signs shown by this form of a blood clot. DVT can be very dangerous when left untreated. In rare cases, the blood clot can break off, travel in the bloodstream, and cause damage to your long. This is what is known as pulmonary embolism or PE. If no medical assistance is sort in time, pulmonary embolism is known to cause:
- shortness of breath
- severe chest pain
- lung damage
- and death in cases of severe lung damage
A blood clot should be treated seriously. They are plenty of option available to help prevent the risk associated with a blood clot and most specifically deep vein thrombosis. A recent study showed that, regardless of having all these effective treatment options to control a blood clot, the study found out that more than half of the patient who was treated for deep vein thrombosis did not receive proper preventive measures against this condition. The risk of getting deep vein thrombosis increases with an increase in age. The condition may also be genetically inherited. This makes DVT more common in people with a family history of the condition. Other factors such as obesity, major surgery, significant injuries, and pregnancy increase the risk of one having this kind of blood clot behind the knee. With DVT, when a blood clot forms, it has the capability of partially or blocking the flow of blood in the vein. Smaller blood clots may cause mild to no symptoms, whereas large clot behind the knee may cause the following symptoms:
- leg swelling
- severe pain especially when standing or walking upstairs
- redness behind knee
- warmth
Signs and symptoms
Doctor Stuart T. Haines says that a small blood clot below the knee is unlikely to cause symptoms. According to the doctor, the clot may, in rare cases, extend or form above the knee. The cot may break away, travel in the bloodstream, and block a blood vessel in the lung. This, as mentioned, is what is known as pulmonary embolism. The signs of a blood clot at the back of the leg behind the knee that breaks and blocks veins in the lung will include the following:
- sudden shortness of breath
- mild to severe coughing
- severe chest pain
Healthcare practitioners and medical researchers say that pulmonary embolism can be life-threatening if not urgently attended to. The complication involved with PE will depend on the size of the blood clot that breaks and blocks the veins in the lung. 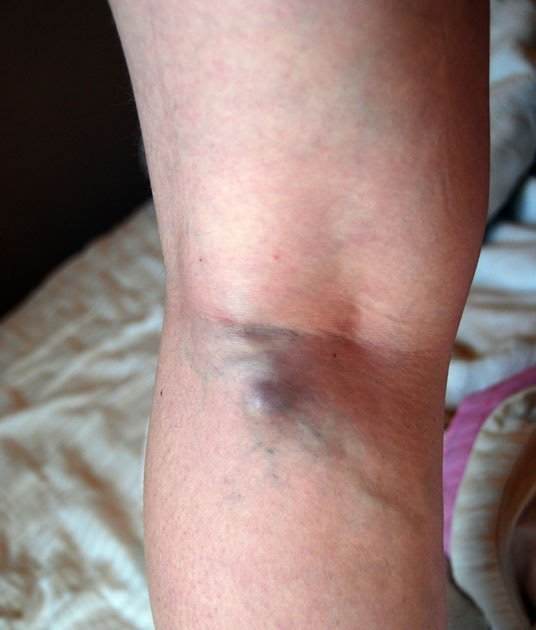 Deep vein thrombosis continues to damage the valves in the leg vein if left unattended. The valve in the leg vein is responsible for making sure the blood flow upwards towards the heart. It is the faction of these valves to ensure that blood does not flow back towards the feet. With DVT, blood pools in the legs instead of flowing upwards towards the heart. The pooling of blood in the feet is responsible for chronic swelling and pain. The pooling may also cause a color change to your legs and cause the development of sores. When this happens, this condition is called post-thrombotic syndrome. The pain caused by the pooling of blood in the feet will often remain even after the blood clot has dissolved. WebMD states that deep vein thrombosis may occur anywhere on the body. It is, however, common in the legs, thighs, and pelvis. Harvard health publication states that clots in the lungs are twice as deadly as a heart attack. A clot is a mechanism through which your body is able to stop blood loss in case of an injury. That is to say, a blood clot comes to the rescue to heal the wound. When, however, the clot is occurring deep inside the vein, this can be problematic. It can cause redness, tenderness, pain, and swelling of the affected limb. The signs and symptoms of a deep vein thrombosis will include the:
Deep vein thrombosis continues to damage the valves in the leg vein if left unattended. The valve in the leg vein is responsible for making sure the blood flow upwards towards the heart. It is the faction of these valves to ensure that blood does not flow back towards the feet. With DVT, blood pools in the legs instead of flowing upwards towards the heart. The pooling of blood in the feet is responsible for chronic swelling and pain. The pooling may also cause a color change to your legs and cause the development of sores. When this happens, this condition is called post-thrombotic syndrome. The pain caused by the pooling of blood in the feet will often remain even after the blood clot has dissolved. WebMD states that deep vein thrombosis may occur anywhere on the body. It is, however, common in the legs, thighs, and pelvis. Harvard health publication states that clots in the lungs are twice as deadly as a heart attack. A clot is a mechanism through which your body is able to stop blood loss in case of an injury. That is to say, a blood clot comes to the rescue to heal the wound. When, however, the clot is occurring deep inside the vein, this can be problematic. It can cause redness, tenderness, pain, and swelling of the affected limb. The signs and symptoms of a deep vein thrombosis will include the:
- pain and tenderness with no known cause
- unexplained swelling at the back of the knee
- redness behind knee
- the area behind the knee may feel warm to touch
- legs cramps at night
- severe joint pain
- fever
- positive Homan’s signs (sharp pain in your calf when your foot is flexed upwards with your knee slightly bent)
If you experience the above symptoms for more than a few hours, you will need to call your doctor as soon as possible. This may help prevent pulmonary embolism (formed when a blood clot breaks and blocks veins in the lung). Pulmonary embolism will have the following signs and symptoms:
- Sudden difficulties in breathing
- Feeling lightheaded, some people may faint
- Abnormal heartbeat (fast or irregular)
- Severe unexplained chest pain or discomfort that worsens with deep breath or coughing
- Low blood pressure
If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned, please call a doctor as soon as possible.
Treatment options
A blood clot can be life-threatening. Urgent medical treatment is required to try and prevent such complications from materializing. How then do you treat a blood clot behind the knee? The treatment of deep vein thrombosis will start with the diagnosis to help identify the extent of the clot.
As a renowned Queens vein doctor states, the timely and effective treatment of blood clots and DVT is crucial in preventing serious complications, including pulmonary embolism and long-term damage to the affected veins.
In the diagnosis of a blood clot, your doctor will take your medical history and perform a physical examination. In most cases, further taste is required to confirm the diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis. This is because the symptoms shown are sometimes the same as those shown by other medical conditions. A common test performed to confirm the diagnosis of DVT will include;
- Duplex Doppler is a medical process that uses the combination of ultrasound (that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images) and a flow probe that shows the direction of the flow of the blood in your vein. This combination help shows any blockage in veins.
- Contrast venography, in this process, your injects a substance in your vein that shows up on x-ray
- A computer tomography CT scan may also help identify a blood clot
- a sample of your blood may also be tested for conditions that increase blood clotting tendency
Here is how to treat a blood clot behind knees
1. Medicine
Minor cases of deep vein thrombosis or blood clot behind the knee are often treated with a medicine known as blood thinners. This medicine works by increasing the time it takes for blood to clot in the body. Other such as anticoagulants help prevent the existing blood clot from becoming larger. With deep vein thrombosis, you can try the following medicines:
Anticoagulation medicine
Anticoagulants prevent blood clots from getting bigger. In cases of DVT, they can help prevent a blood clot from breaking off and becoming lodged in another part of the bloodstream, more specifically those in the lungs. Anticoagulants are often referred to as thinning drugs; they, however, do not thin the blood but alter the protein within the blood, which prevents blood clots from forming fast.
Heparin
Heparin is another commonly used anticoagulant. This medicine is prescribed first as it works immediately. This medicine is available in two different forms, standard heparin (unstructured) and low molecular weight heparin. Standard heparin can be given as an intravenous injection (administered straight into the vein), intravenous infusion (continuous drip is fed into your arms vein), or administered as a subcutaneous injection, which is an injection under your skin. Low molecular weight heparin, on the other hand, is often administered as a subcutaneous injection. The dose will vary from person to person; as such, they have to be monitored and adjusted if necessary.
Warfarin
Warfarin is the other medicine used to treat blood clot behind the knee. This medicine, unlike heparin, is taken as a tablet. To prevent further blood clots, you may need to take it after initial treatment with heparin. In most cases, your doctor will recommend you take medicine for three to six months. In a rare case, you may need to take it for a longer time or even for life. The effects of this medicine may vary from person to person. You will need to be closely monitored by having a frequent blood test to ensure you’re taking the right dosage. Warfarin can be affected by your diet, and as such, you will need to:
- Maintain a constant diet in the course of treatment
- Cut down on alcohol consumption
- Do not change the timing of your dosage
- Confirm with your doctor before you can start taking other medicine
- Do not mix with herbal drugs
Rivaroxaban
Rivaroxaban, a medicine recommended by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence As a possible treatment for adults with deep vein thrombosis. The medicine is also recommended to help prevent recurrent cases of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Rivaroxaban is categorized as a directly acting oral anticoagulant. The drug helps prevent blood clot by inhibiting factor Xa that restrict the formation of thrombi- an enzyme that helps the blood clot.
Apixaban
Apixaban is another drug recommended by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence NICE. The drug is used as a possible method to treat and prevent DVT and pulmonary embolism. Like rivaroxaban, this drug is taken orally as a tablet and prevent blood clot forming by hindering factor Xa that restrict the formation of thrombin.
2. Surgery
Surgery to treat a blood clot behind the knee is rarely used. In most cases, your healthcare provider will recommend surgery if the blood clot is very large and is blocking a major blood vessel. When not performed correctly, surgery increases the risk of forming new blood clots.
3. Self-care
At home, you can prevent pain and swelling by:
- Wearing compression stocking. We recommend Terramed Extra Firm Opaque Graduated Compression Pantyhose (Check price on Amazon)
- Performing regular excesses
- Avoid holding your leg in the same position for long
- Instated of using the elevator, try walking the stairs for the time being
- Cut down on your weight as obesity and overweight may increase the risk of developing this kind of blood clot
- Stop smoking and consuming a lot of alcohol
References
- Deep-vein blood clots, know the signs: http://www.health.harvard.edu/heart-health/deep-vein-blood-clots-know-the-signs
- What everyone should know about blood clots: https://health.clevelandclinic.org/2014/01/what-everyone-should-know-about-blood-clots/
- Preventing a hidden danger of joint surgery, blood clots: http://www.everydayhealth.com/columns/health-answers/how-to-avoid-a-blood-clot-after-orthopedic-surgery/
- Treating deep vein thrombosis: http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Deep-vein-thrombosis/Pages/Treatment.aspx